Overview
For in vivo neuroscience optogenetics research, scientists may have the needs to target individual neurons, multiple ROIs or large-scale brain areas for optogenetic stimulation of one or more opsins in awake, head-fixed or freely behaving animals.
For more details, please click
“Patterned Illumination Systems for Cellular-Resolution Optogenetics in Neuroscience” here➡️

Key System Requirements
- Quick and easily integratable with existing experimental rigs/setups
- Ability for widefield and/or targeted stimulation of cellular and/or subcellular features
- Ability to access multiple brain regions simultaneously at variable depths
- Ability to stimulate multiple ROIs at physiologically relevant speeds
- Ability to stimulate multiple opsins (multi-color)
- Easy software control to adjust light intensity and frequency
Polygon DMD Pattern Illuminator
Mightex offers a wide selection of optogenetics solutions ranging from basic LED light sources to full optogenetics modules including our market-leading Polygon DMD device for patterned stimulation, which has been adopted by over 650 research labs worldwide and led to over 100 scientific papers. Please contact our applications specialists to discuss your needs and find out how Mightex can help you with your next scientific breakthrough.

Research Highlights using Mightex Solutions
In this video, the OASIS Implant with the Polygon Pattern Illuminator is being used to target specific parts of the cortex with optogenetic stimulation (top right corner) in a freely-behaving animal. The optogenetic stimulation corresponds to a behavioural response, and this changes depending on where the optogenetic stimulation is targeted.
For more details, please click here!
Dr. Noaf Salah & Prof. Zhigang He
Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA


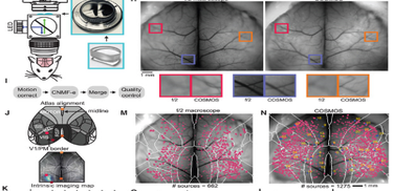
The authors introduced an optical method, COSMOS, to track neural activity in the dorsal neocortex of awake mice during a motor task. This approach revealed spatially distributed neuronal population representations across the cortex, encoding precise information about ongoing motor actions on single trials, suggesting widespread information sharing between cortical areas in the processing of motor plans. Simultaneous optogenetic inhibition of multiple brain regions was achieved using Mightex’s Polygon DMD pattern illuminator on the OASIS Macroscope with a large field of view.


Isaac V. Kauvar & Prof. Karl Deisseroth
Stanford University, Stanford, USA
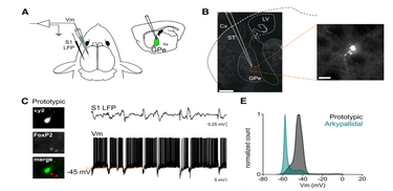
In the mouse external globus pallidus (GPe), two main neuronal subpopulations, prototypic and arkypallidal cells, exhibit differences in their cellular properties. Through in vivo whole-cell recordings and optogenetic stimulation, researchers found that these subpopulations display distinct synaptic connectivity patterns, with prototypic cells being strongly targeted by subthalamic nucleus (STN) and indirect pathway medium spiny neurons (MSNs), while direct pathway MSNs selectively inhibit arkypallidal cells.
Maya Ketzef & Prof. Gilad Silberberg
Karolinska Institute, Solna, Sweden


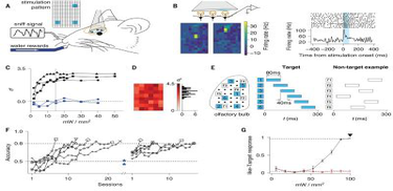
The study investigated how neural activity contributes to perception by training mice to recognize synthetic odors through optogenetic activation. The researchers identified that the most predictive factors for recognition were sequences of spatially identified units ordered by latencies, shedding light on the fundamental logic of the olfactory code and offering a general framework for exploring the relationship between sensory activity and perception. This study used Mightex’s Polygon DMD device for patterned optogenetic stimulation.


Edmund Chong & Prof. Dmitry Rinberg
NYU, New York, USA
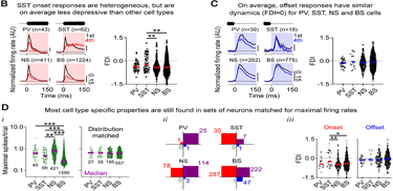
In the study conducted on awake mice exposed to repeating noise burst stimuli, researchers examined the short-term history-dependence of both sound onset and offset responses in the auditory cortex (AC). They found that offset responses are generally less depressive than onset responses, and the dynamics of these responses varied among cell types, with distinct patterns observed in PV and SST interneurons. The study concludes that the history-dependence of onset and offset responses differs and suggests implications for the encoding of ongoing sound stimuli in the AC.
Timothy Olsen & Prof. Andrea R. Hasenstaub
University of California-San Francisco, California, USA